What you’ll need
- A Google account
- A YouTube channel (to fetch from)
- 10–15 minutes
Step 1 — Open Google Cloud Console
- Go to https://console.cloud.google.com and sign in.
- If prompted, accept the terms and set a country.
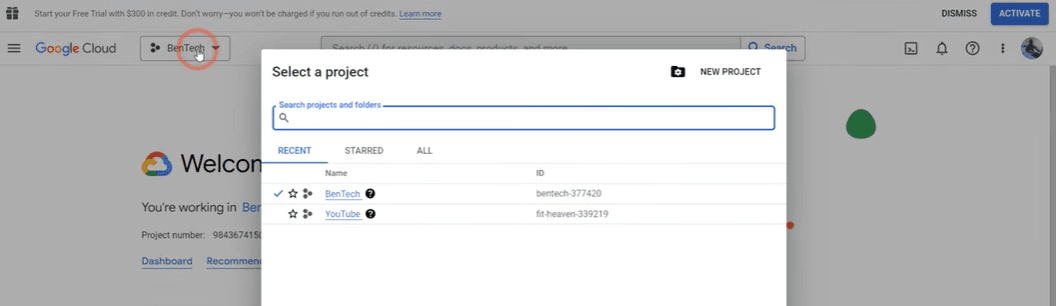
Step 2 — Create (or select) a project
- In the top navbar, click the Project selector (usually shows your current project name).
- Click New Project → give it a name (e.g.,
MyProject) → Create. - Select your new project.
Step 3 — Enable the YouTube Data API v3
- In the left sidebar, go to APIs & Services → Library.
- Search for YouTube Data API v3.
- Click it → Enable.
Step 4 — Create credentials (API key)
- Go to APIs & Services → Credentials.
- Click + CREATE CREDENTIALS → API key.
- A dialog will show your API key. Copy it (you can regenerate later if needed).
Step 5 — (Recommended) Restrict your API key
- In the API keys list, click the key you just created.
- Under Application restrictions, choose HTTP referrers (web sites).
- Add allowed origins, e.g.:
https://koshurcoder.in/*http://localhost:3000/*(for local dev)
- Under API restrictions → Restrict key → choose YouTube Data API v3.
- Click Save.
Step 6 — Find your YouTube Channel ID
- If your channel URL looks like
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCxxxxxxxx…, your Channel ID is the value after/channel/. - If your URL looks like
https://www.youtube.com/@koshurcoder, that’s a handle. You can grab the Channel ID by:- Opening your channel → Right‑click → View page source → search for
channelId. - Or use any trusted “Channel ID lookup” tool.
- Opening your channel → Right‑click → View page source → search for
Step 7 — Test the API in your browser
Paste this into your browser, replacing YOUR_CHANNEL_ID and YOUR_API_KEY:
https://www.googleapis.com/youtube/v3/search?part=snippet&channelId=YOUR_CHANNEL_ID&maxResults=6&order=date&type=video&key=YOUR_API_KEY
You should see a JSON response with an items array containing your latest videos.
If you see an error (e.g., 400 Bad Request), double‑check your channel Id, key, and that the API is enabled for the correct project.
Step 8 — Add environment variables to your site
Create (or update) .env.local in your project root:
NEXT_PUBLIC_YT_API_KEY=AIzaSy...your-keyNEXT_PUBLIC_YT_CHANNEL_ID=UCxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Step 9 — Helper function to fetch videos (TypeScript)
Step 10 — Render videos (Next.js App Router)
In src/app/page.tsx (server component):
Common errors & fixes
- 400 Bad Request: Usually a bad
channelIdor missingtype=video. Verify the URL and that the API is enabled for the correct project. - 403: quotaExceeded: Reduce request frequency or request more quota in Google Cloud.
- API key works locally but not in prod: Check HTTP referrer restrictions include your production domain.
undefinedenv vars:.env.localmust be in project root; keys must start withNEXT_PUBLIC_to be available to the browser.
You’re done ✅
You now have a locked‑down API key, a working fetch helper, and a Next.js page that renders your latest YouTube videos. Swap the styling as you like, and keep an eye on quota usage.